Digital Twins: Revolutionizing Design and Production
Author: Константин Федоров
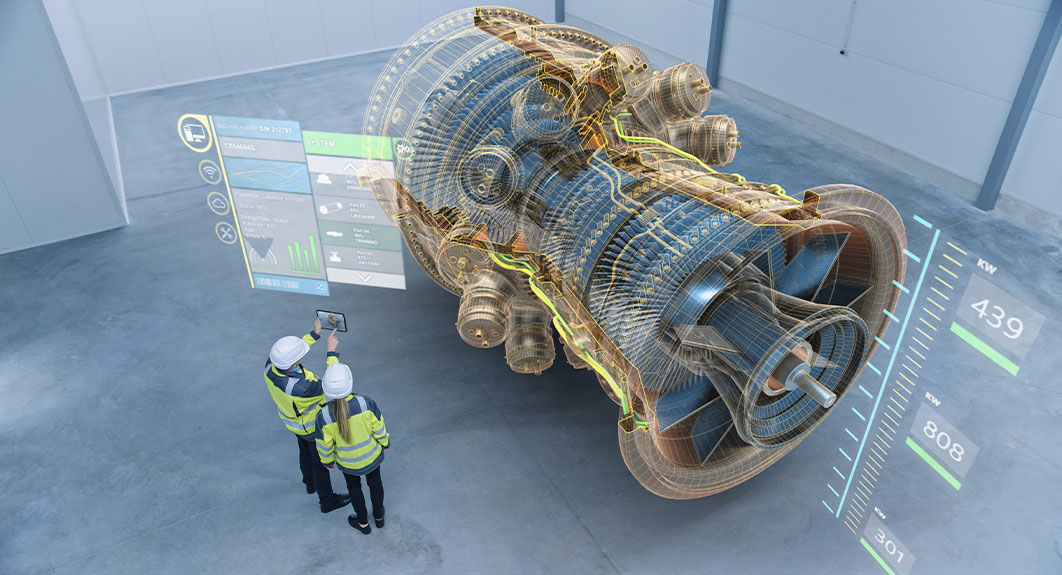
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, the concept of digital twins is emerging as a game-changer in the fields of design and production. A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical object, system, or process that allows businesses to simulate, analyze, and optimize their operations in ways that were previously unimaginable. This technology is transforming how products are designed, tested, and manufactured, leading to innovations that are more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable.
At its core, a digital twin is created by gathering data from sensors embedded in a physical object or system. This data is then used to build a precise digital model that mirrors the real-world counterpart in real-time. Engineers and designers can interact with the digital twin just as they would with the physical object, but with the added ability to test scenarios, predict outcomes, and make adjustments without any physical changes or disruptions to actual operations.
In the realm of design, digital twins are making a significant impact by enabling a more iterative and flexible process. Designers can create and refine products in the virtual environment, testing different materials, shapes, and functions before any physical prototype is built. This not only speeds up the design process but also reduces the costs associated with trial-and-error methods. By simulating how a product will perform under various conditions, digital twins help ensure that the final design is optimized for both performance and manufacturability.
Production processes are also being revolutionized by digital twins. Manufacturers can use digital twins to monitor and optimize production lines, predict maintenance needs, and avoid costly downtime. For instance, by simulating the wear and tear on machinery, a digital twin can alert operators to potential failures before they occur, allowing for preemptive maintenance and minimizing disruptions. This predictive capability extends to the supply chain as well, where digital twins can help manage inventory, reduce waste, and improve logistics.
Moreover, digital twins are paving the way for more sustainable production practices. By optimizing the use of materials and energy, companies can reduce their environmental footprint. For example, a digital twin can simulate the entire lifecycle of a product, from raw material extraction to disposal, allowing businesses to design products that are not only efficient to produce but also easier to recycle or repurpose. This holistic approach to design and production is becoming increasingly important as companies strive to meet environmental regulations and consumer demands for sustainability.
The benefits of digital twins extend beyond individual products or processes. In complex industries such as aerospace, automotive, and energy, digital twins are being used to manage entire ecosystems. For example, an aerospace company might use digital twins to simulate the operation of an entire fleet of aircraft, optimizing fuel efficiency, maintenance schedules, and safety protocols across the board. This system-level approach is helping businesses achieve greater operational efficiency and competitiveness in their respective markets.
In conclusion, digital twins are revolutionizing the way we approach design and production. By providing a virtual counterpart to physical objects and systems, they enable more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable operations. As technology continues to advance, the use of digital twins is likely to become even more widespread, driving innovation and transforming industries around the world.
Popular Articles